Navigating your IRS account tax transcript can feel daunting, but it’s a powerful tool for understanding your tax status, payments, and IRS actions. This guide breaks down the process into clear, actionable steps to help you read and interpret your tax transcript with confidence. Whether you’re tracking a refund, verifying payments, or resolving tax issues, this guide covers everything you need to know.

What Is an IRS Account Tax Transcript?
An IRS account tax transcript provides a detailed record of your tax account, including your balance, payments, adjustments, and transactions made after your tax return was filed. Unlike other IRS transcripts, the account transcript focuses on financial activity and IRS processing details, making it essential for tracking your tax obligations or refunds.
By following this guide, you’ll learn how to access, read, and understand your IRS account tax transcript to make informed financial decisions.
Step 1: Access Your IRS Account Tax Transcript
To begin, you’ll need to obtain your tax transcript. Here’s how:
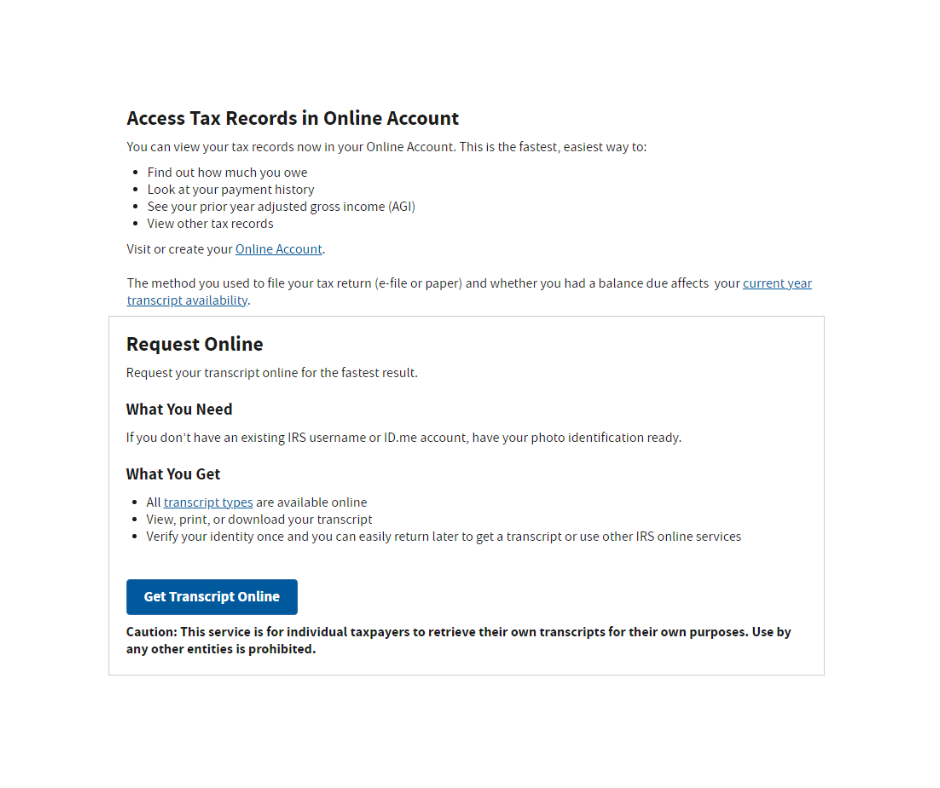
- Online Access: Visit irs.gov/transcripts to log in or create an IRS account. You’ll need to provide personal identification, financial verification (e.g., credit card or loan details), and a registered phone number for authentication.
- Mail or Phone Request: If you prefer, request a mailed copy using the address from your most recent tax return or call the IRS automated phone service at 1-800-908-9946.
- Pro Tip: Online access is faster, typically providing instant results, while mailed copies may take 5-10 days.
Keyword Tip: Searching “IRS account tax transcript” or “get IRS transcript online” can help you find the official IRS portal quickly.
Step 2: Confirm You Have the Right Transcript
The IRS offers several types of transcripts, so ensure you’re reviewing the Tax Account Transcript. This document details:
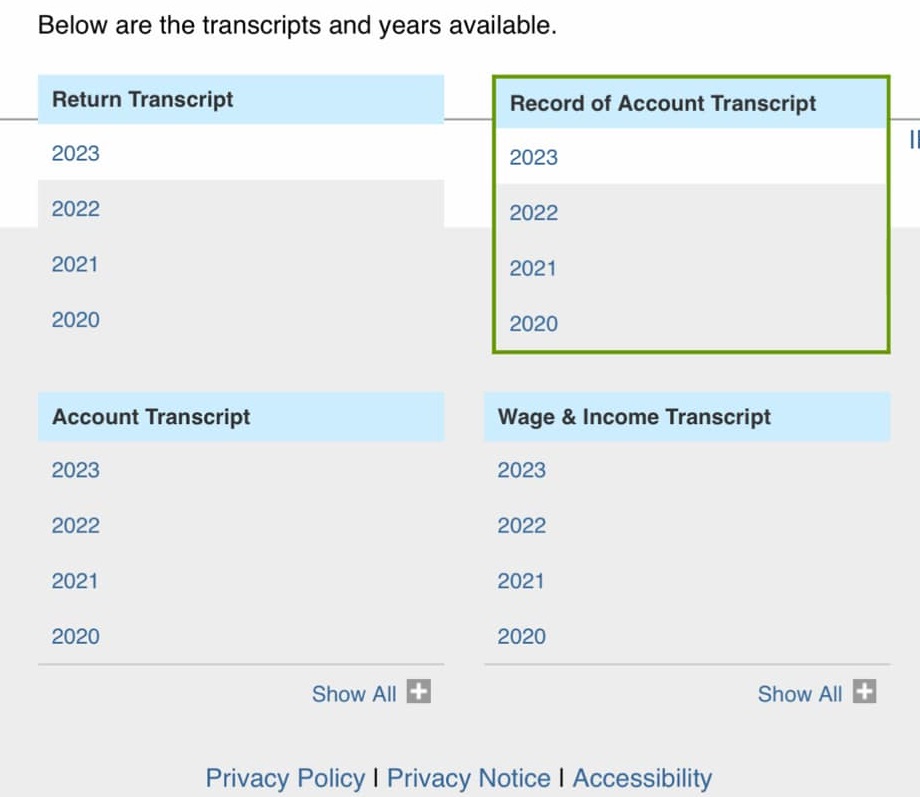
- Tax balance
- Payments made
- Adjustments
- Transactions post-filing
Other transcripts, like the Tax Return Transcript or Wage and Income Transcript, serve different purposes. Double-check the title to avoid confusion.
Step 3: Verify Identifying Information
At the top of your transcript, you’ll find key identifying details. Confirm these match your records:
- Name
- Masked Social Security Number (SSN)
- Filing status (e.g., single, married filing jointly)
- Tax year
If any information is incorrect, contact the IRS immediately to resolve discrepancies.
Step 4: Review the Return Summary Data

The summary section provides a snapshot of your tax return. Look for:
- Taxable Income: Your income subject to tax.
- Adjusted Gross Income (AGI): Your total income minus specific deductions.
- Filing Status: Confirms how you filed (e.g., single, head of household).
- Balance Due or Refund: Indicates if you owe money or are due a refund.
These figures are critical for understanding your tax obligations or refund status.
SEO Tip: Use terms like “IRS transcript taxable income” or “check IRS refund status” to research specific details online.
Step 5: Decode IRS Transaction Codes
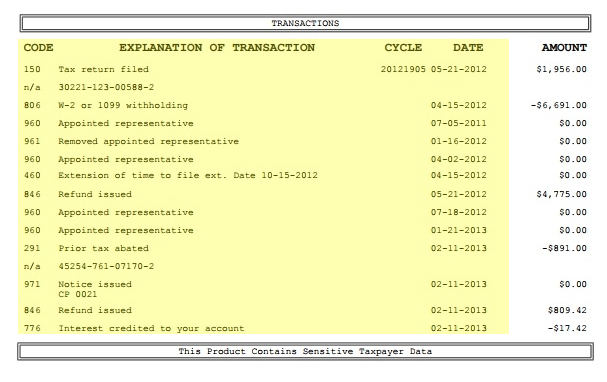
The heart of the tax account transcript lies in its transaction codes, three-digit numbers that describe specific IRS actions. Here are some common codes to know:
- Code 150: Tax return filed and tax assessed.
- Code 570: Refund hold placed (often due to additional review).
- Code 571: Refund hold released.
- Code 766/768: Credits applied to your account (e.g., Earned Income Tax Credit).
- Code 846: Refund issued.
Each code is accompanied by a date, amount, and brief description. Cross-reference unfamiliar codes with the IRS’s Transaction Code Pocket Guide for clarity.
Step 6: Understand Cycle Codes
Cycle codes indicate when the IRS processed your return or account updates. For example, a cycle code like 20241605 breaks down as:
- 2024: The tax year.
- 16: The IRS cycle week (16th week of the year).
- 05: The day of the week (e.g., Friday).
These codes help you track the timing of IRS actions, such as when a refund was processed or a payment was recorded.
Step 7: Track Payments and Adjustments
This section lists all financial activity, including:
- Payments you’ve made (e.g., estimated tax payments).
- Credits applied (e.g., stimulus payments or tax credits).
- Adjustments (e.g., corrections to your return).
- Holds placed or released.
Compare these entries with your records to ensure accuracy. Discrepancies may indicate errors or pending IRS actions.
Step 8: Confirm Resolution or Outstanding Items
Look for codes indicating the status of your account:
- Refund Issued: Code 846 confirms your refund has been sent, with the amount and date.
- Holds Released: Codes like 571 indicate resolved issues.
- Balance Due: Entries showing amounts owed may include penalties or interest.
If you see unresolved issues or unclear codes, consult the IRS website or a tax professional for further clarification.
Additional Tips for Reading Your IRS Account Tax Transcript
- Use IRS Resources: The IRS website offers detailed explanations of transaction codes and transcript terms. Bookmark their transcript FAQ page for quick reference.
- Understand Masked Data: For security, personal information like SSNs may be partially masked. Financial data, however, remains unmasked for verification.
- Seek Professional Help: If the transcript is complex or unclear, consult a tax professional for a thorough analysis.
- Check Regularly: Monitoring your transcript periodically ensures you catch errors or updates early, especially during tax season.
Why Understanding Your Tax Transcript Matters
Reading your IRS account tax transcript empowers you to:
- Track refund status and payment history.
- Identify and resolve IRS holds or issues.
- Verify the accuracy of your tax records.
- Make informed decisions for future tax planning.
By mastering these steps, you’ll gain confidence in managing your tax obligations and avoiding costly mistakes.
Conclusion
Your IRS account tax transcript is a valuable tool for staying on top of your tax status. By accessing the transcript, verifying key details, and decoding transaction and cycle codes, you can ensure your financial records align with IRS data. If you encounter challenges, leverage IRS resources or consult a tax professional for expert guidance.
For more information, visit irs.gov/transcripts to access your transcript today and take control of your tax records.
